Find Your Perfect Farming Zone Today
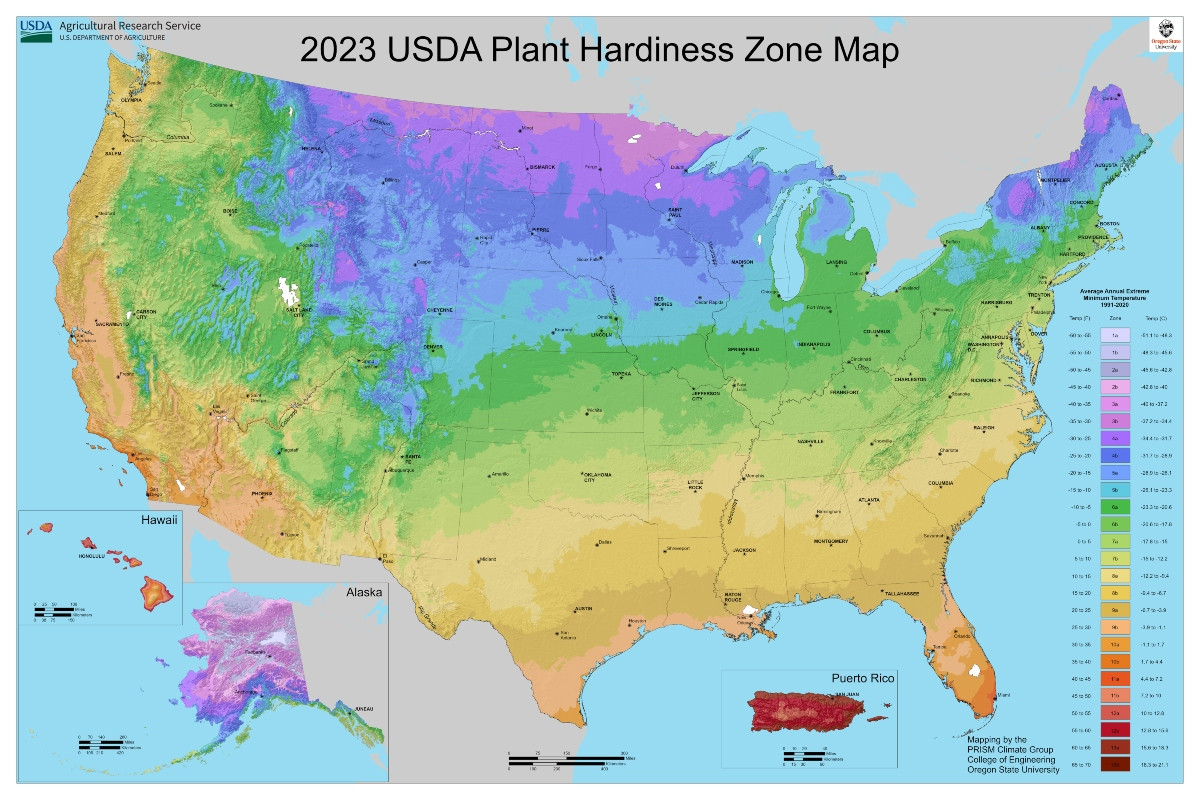
Ever wondered, “What farming zone am I in?", and how it could influence your field agriculture? Whether you're a seasoned farmer or just starting out, understanding your farming zone is crucial for successful crop selection, implementing the best planting practices, and more. Let’s dive into the world of farming zones and discover how to maximize your agricultural yields.
Understanding Farming Zones
So, what exactly is a farming zone? A farming zone is a geographical area defined by specific climatic conditions, which significantly impact agricultural practices and crop selection for climate. These zones help farmers decide what to plant and when to plant based on climatic variables like temperature, precipitation, and soil type.
Imagine your farm as a puzzle. Each piece of the puzzle represents a different aspect of your terrain—the weather, soil, sunlight, and water. When you know what farming zone you are in, you can fit these pieces together to create a thriving agricultural landscape. Changing zone agricultural practices might seem daunting, but with the right information, it can be a game-changer.
Why Knowing Your Farming Zone Matters
Understanding your farming zone is like having a map in unexplored territory. It guides you through the complexities of field agriculture, ensuring that you make informed decisions. For instance, if you’re in a colder zone, you might need to consider crops that thrive in lower temperatures, such as winter wheat or barley.
On the flip side, if you’re in a warmer climate, your **crop selection for climate** might lean towards heat-resistant crops like corn or peppers. Tailoring your agricultural practices to your specific farming zone can drastically improve your yields and profitability.
Best Planting Practices by Farming Zone
Let's explore some of the best planting practices based on different farming zones. Remember, the key to successful farming is adaptability. Each zone has its unique challenges and opportunities, and knowing your farming zone is the first step to mastering your field agriculture.
In colder zones, where the growing season is shorter, early planting can make a significant difference. Planting seeds as soon as the soil is workable can give your crops a head start. Additionally, using techniques like crop rotation and cover cropping can help improve soil health and reduce the risk of pests and diseases.
In warmer zones, where the growing season is longer, planting can be done over a more extended period. However, it’s essential to choose the right time of year based on your specific crops. For example, planting heat-sensitive crops in the cooler parts of the year can help them thrive. Water management is also crucial in warmer zones, ensuring that crops receive the right amount of moisture without being overwatered.
Tips for Changing Zone Agricultural Practices
Changing your agricultural practices based on different farming zones can seem overwhelming, but with the right strategies, you can make the transition smooth and successful. Start by assessing your current practices and identifying areas for improvement. Then, research the best practices for your new farming zone and gradually implement them.
For example, if you’re moving from a warmer to a cooler zone, you might need to invest in greenhouses or other protective structures to extend your growing season. Similarly, if you’re moving from a cooler to a warmer zone, you might need to upgrade your irrigation system to handle higher water demands.
Optimizing Crop Selection for Climate
Crop selection for climate is a critical aspect of field agriculture. Different crops thrive in different climatic conditions, so knowing your farming zone can help you choose the right crops for your land. For instance, if you’re in a zone with high rainfall, you might consider crops that are tolerant to waterlogging, such as rice or watercress.
The Impact of Soil Type on Farming Zones
Soil type is another crucial factor to consider when determining your farming zone. Different soils have varying nutrient content and water-holding capacities, which can affect crop growth. For example, clay soils tend to hold more water and nutrients but can be susceptible to waterlogging. Sandy soils, on the other hand, drain quickly but may require more frequent irrigation.
Understanding your soil type can help you make better **crop selection for climate** decisions. For instance, if you have sandy soil, you might choose drought-resistant crops like sorghum or millet. If you have clay soil, you might opt for crops that can handle wetter conditions, like wheat or soybeans.
Conclusion
So, have you determined what farming zone you are in? By understanding your farming zone, you can make informed decisions about crop selection, planting practices, and more. Whether you're planting in a cooler northern climate or a warmer southern one, knowing your zone is the first step to a bountiful harvest.
Ready to take your field agriculture to the next level? Start by researching your farming zone and adjusting your practices accordingly. You’ll be amazed at the difference it can make. Dive in, assess your land, and watch your crops thrive.
FAQs
1. How do I determine my specific farming zone?
You can determine your farming zone by consulting agricultural maps or using online resources that provide detailed information on different farming zones. Local agricultural extensions or government agencies can also provide valuable insights.
2. Can farming zones change over time?
Yes, farming zones can change due to climate change, deforestation, and other environmental factors. It's essential to stay updated with the latest information to adapt your agricultural practices accordingly.
3. What are some common mistakes farmers make regarding their farming zone?
Some common mistakes include using incorrect planting techniques, choosing unsuitable crops for their zone, and failing to manage water and soil nutrients efficiently. Staying informed and adapting to your specific zone is key to avoiding these pitfalls.
4. How does soil type affect my farming zone?
Soil type affects your farming zone by influencing water retention, nutrient availability, and drainage. Understanding your soil type helps in selecting appropriate crops and implementing proper agricultural practices.
5. What resources are available for learning about farming zones?
There are numerous resources available, including agricultural textbooks, online courses, local farming workshops, and government agricultural services. Websites like the USDA and FAO provide detailed information and guidelines on farming zones and best practices.
```
0 Response to " Find Your Perfect Farming Zone Today"
Post a Comment