Discover Plant Cellular Respiration
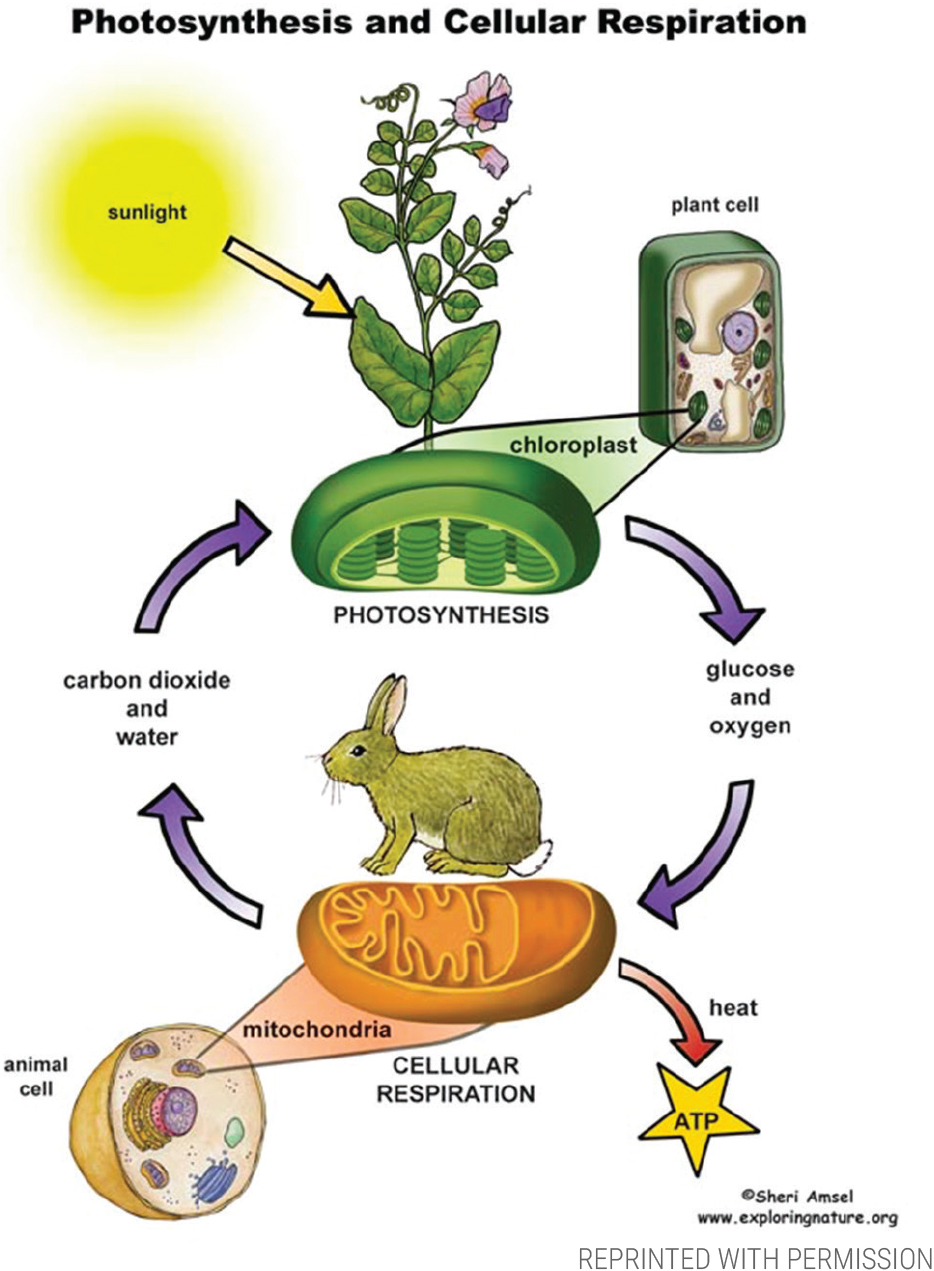
Ever wondered how plants manage to stay alive, grow, and reproduce? You might think it’s all about photosynthesis, but there’s another crucial process happening inside every plant cell: cellular respiration. Just like animals and humans, plants need energy to survive, and this energy is harnessed through cellular respiration. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of plant cellular respiration and discover how this process fuels life.
What is Cellular Respiration?
Imagine cellular respiration as the engine of a car. Just as an engine converts fuel into motion, cellular respiration converts glucose into adenosine triphosphate (ATP)—the energy currency of the cell. This process is essential for all living organisms, including plants. But how exactly do plants perform cellular respiration?
The Three Stages of Cellular Respiration
Plant cellular respiration happens in three main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle (also known as the citric acid cycle), and the electron transport chain. Each stage plays a crucial role in converting glucose into energy.
Glycolysis: The First Step
Glycolysis is the first step in the process cell metabolism. It occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and involves breaking down glucose into pyruvate. This stage generates a small amount of ATP and NADH, a molecule that carries high-energy electrons. Think of glycolysis as the initial spark that ignites the cellular respiration process.
The Krebs Cycle: The Next Phase
The Krebs cycle takes place in the mitochondria, often referred to as the “powerhouse” of the cell. In this stage, pyruvate is further broken down into carbon dioxide and involves the production of more ATP and NADH. It’s like the middle gear in a bicycle, keeping the process moving smoothly and efficiently.
The Electron Transport Chain: The Final Stage
The final stage occurs in the mitochondrial membrane. Here, the high-energy electrons carried by NADH and FADH2 are transferred through a series of protein complexes, generating a significant amount of ATP. This stage is akin to the final push that gets a bicycle up a steep hill, providing the bulk of the energy needed for cellular activities.
Resources Behind the Process
Understanding the resources involved in plant cellular respiration is crucial. Plants obtain glucose from photosynthesis, where they convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose and oxygen. This glucose then serves as the primary resource for cellular respiration, powering the various stages of energy production.
Difference Between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
Do plants undergo aerobic respiration, or do they sometimes switch to anaerobic respiration? Aerobic respiration requires oxygen and is the primary method used by plants to produce ATP. However, in oxygen-deprived conditions, plants can switch to anaerobic respiration. This process is less efficient and produces less ATP, often resulting in byproducts like lactic acid.
The Role of Mitochondria in Plant Cellular Respiration
Mitochondria are the key players in the aerobic respiration process. They convert the chemical energy from glucose into ATP through the Krebs cycle and electron transport chain. Inside the mitochondria, biochemists termed enzymes work in perfect harmony to ensure smooth energy production every second.
Unlocking the Secrets of Plant Cellular Respiration
Now that you understand the basics of plant cellular respiration, you might be curious about how this process influences plant growth and health. Cellular respiration is a fundamental aspect of plant physiology, driving everything from photosynthesis to reproduction.
Applying Your Knowledge
Next time you see a plant thriving in your garden or a tree standing tall, remember that behind its beauty lies a complex network of cellular respiration, continually producing ATP to fuel life’s vital processes. The more you learn about this incredible process, the deeper your appreciation for the natural world will grow.
The Future of Plant Cellular Respiration Research
Scientists are continuously exploring new methods to enhance plant cellular respiration. By understanding and optimizing this process, we can develop more resilient crops and sustainable agriculture practices. Imagine a world where plants can efficiently convert sunlight into energy, reducing our reliance on fossil fuels. This is not just a dream; it’s a reality that scientists are working to achieve.
Do Plants Need Cellular Respiration?
Absolutely! Cellular respiration is the backbone of plant metabolism. Without it, plants would struggle to survive, grow, and reproduce. So the next time you wonder, “Do plants do cellular respiration?” you can confidently say, “Yes, and it’s a vital part of their existence!”
Conclusion
Plant cellular respiration is a captivating process that fuels the life of every plant. From converting glucose into adenisine triphosphate to the role of mitochondria in aerobic respiration, the journey of energy production in plants is truly remarkable. By understanding this process, we gain insight into the intricate workings of nature and the resources that sustain life. Let’s continue to explore and appreciate the wonders of plant cellular respiration. Dive deeper into the fascinating world of plant metabolism, and click here to learn more about the amazing science behind life’s energy.
FAQs
Q1: What are the main products of plant cellular respiration?
The main products of plant cellular respiration are ATP (adenosine triphosphate), carbon dioxide, and water. ATP is the energy currency of the cell, while carbon dioxide and water are byproducts of the process.
Q2: Why is cellular respiration important for plants?
Cellular respiration is crucial for plants because it provides the energy needed for growth, reproduction, and other vital processes. Without cellular respiration, plants would not be able to convert glucose into usable energy.
Learn more about cellular respiration in plants
Q3: Can plants perform anaerobic respiration?
Yes, plants can perform anaerobic respiration in the absence of oxygen. However, this process is less efficient and produces less ATP. It often results in byproducts like lactic acid, and it is only a temporary solution in oxygen-deprived conditions. For more detailed information, check out this research paper.
Q4: What happens during glycolysis in plant cells?
Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration and occurs in the cytoplasm of plant cells. In this stage, glucose is broken down into pyruvate, generating a small amount of ATP and NADH. This process sets the stage for the subsequent steps of the Krebs cycle and electron transport chain.
```
0 Response to " Discover Plant Cellular Respiration"
Post a Comment