Discover Plant Cells Mitochondria Functions
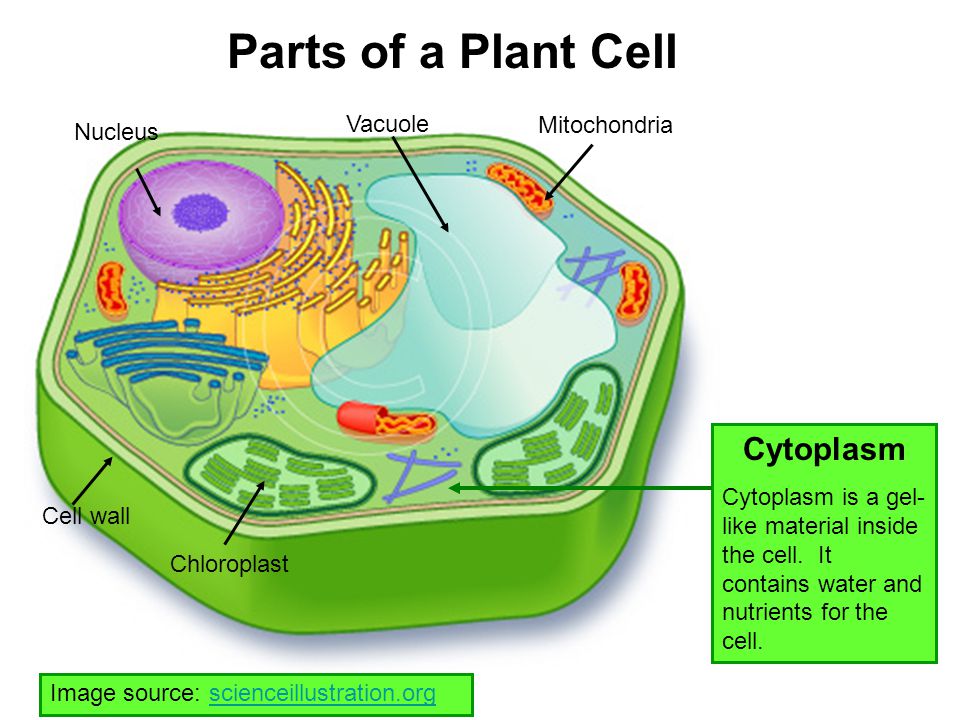
Imagine if your living room were a bustling city where every room served a crucial purpose. Each room has a specific job, like the kitchen for cooking and the bedroom for resting. Similarly, within plant cells, mitochongria play a pivotal role in the cells’ energy production. But have you ever wondered how these tiny powerhouses, or organelles, create the fuel that keeps plants alive? Let’s dive in and explore the fascinating world of have plant cells mitochondria and unravel their essential functions.
What Are Mitochondria?
Mitochondria, often referred to as the "powerhouses of the cell," are small, specialized organcells found within both plant and animal cells. These tiny wonders are responsible for converting nutrients into energy that the plant can use. But how do they do it? The process is a bit like turning a raw potato into a delicious, energy-rich meal. It involves complex biochemical reactions that transform glucose into a usable form of energy.
To understand the intricate dance of these energy-converting factories, let’s break it down into simpler steps. When you think of a bustling kitchen where ingredients are transformed into a feast, imagine mitochondria as the master chefs.
The Role of Mitochondria in Plant Energetic Basis
Within plant cells, mitochondria play a central role in cell respiration, a process analogous to cellular breathing. This process involves multiple steps that convert glucose into energy-rich molecules. But did you know that these mitochondria are the workhorses that keep the plant running smoothly, day and night? Unlike Chloroplasts and Mitochondria, which rely on sunlight for energy, mitochondria operate regardless of the time of day, ensuring a steady supply of energy.
Imagine mitochondria as miniature furnaces that burn glucose molecules to produce energy. The process starts with breaking down glucose in the cytoplasm and continues through several stages in the mitochondria. The ultimate goal is to produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the universal energy currency of the cell. This ATP production is critical for the plant's survival and growth.
How Do Mitochondria Produce Energy?
Let’s delve deeper into the three main stages of cellular respiration that occur within mitochondria:
- Glycolysis: This is the first stage, taking place in the cytoplasm. Glucose is broken down into pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP.
- Krebs Cycle: Happening in the mitochondrial matrix, pyruvate is further broken down, releasing carbon dioxide and producing more energy-rich molecules.
- Electron Transport Chain (ETC): Occurring in the inner mitochondrial membrane, the ETC utilizes the energy from previous stages to pump protons and generate ATP. This is the final, critical step in energy production.
These steps are a bit like an assembly line, where each stage builds on the last to produce the final product: ATP. The continuous production of ATP ensures that the plant has the energy it needs to grow, reproduce, and respond to its environment.
Chloroplasts and Mitochondria: A Dynamic Duo
While mitochondria are crucial for cells’ energy production, they often work hand-in-hand with another organelle: chloroplasts. Have you ever noticed how plants need both sunlight and oxygen to thrive? Chloroplasts handle photosynthesis, converting sunlight into chemical energy stored in glucose. Mitochondria then use this glucose to produce ATP, completing the energy cycle.
Think of chloroplasts and mitochondria as a dynamic duo. Chloroplasts act like solar panels, capturing energy from the sun, while mitochondria are like batteries, storing and distributing that energy. Together, they form the energetic basis of plant life.
The Importance of Mitochondria in Plant Physiology
Mitochondria are not just about energy production. They also play a crucial role in other cellular processes, such as cell signaling and apoptosis (programmed cell death). This flexibility makes mitochondria indispensable for plant health and resilience.
Let’s take a closer look at how mitochondria communicate within the cell. They send and receive signals that help regulate growth, development, and stress responses. For example, during drought or extreme temperatures, mitochondria can trigger defense mechanisms to protect the plant. It’s like having a built-in alarm system that alerts the cell to potential dangers and prepares it for survival.
Why Does Mitochondrial Health Matter?
Maintaining the health of mitochondria is vital for the overall well-being of the plant. Any dysfunction in mitochondrial activity can lead to reduced growth, poor yield, and increased susceptibility to diseases. Therefore, understanding and supporting mitochondrial function is crucial for optimizing plant productivity.
Conclusion
As we've explored, have plant cells mitochondria are far more than just energy generators. They are intricate, multifunctional organelles that keep the plant’s metabolic engine running smoothly. From converting glucose into ATP to communicating within the cell, mitochondria are essential for plant survival and growth. So the next time you see a plant, remember the tiny, powerful mitochondria working tirelessly to keep it thriving.
To delve deeper into the fascinating world of plant cells and their organelles, feel free to explore additional insights from reputable sources like Nature Reviews Genetics and Trends in Plant Science. Now, go ahead and click to uncover more about the mysteries of plant life and the tiny powerhouses that make it possible!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the role of mitochondria in plants?
Mitochondria in plants are primarily responsible for ATP production through cellular respiration, providing the energy needed for the plant's growth and survival.
2. How do mitochondria and chloroplasts work together?
Chloroplasts and Mitochondria work in tandem to maintain the plant’s energetic balance. Chloroplasts capture sunlight to produce glucose, which mitochondria then convert into ATP through respiration.
3. Can plants survive without mitochondria?
No, plants cannot survive without mitochondria. Mitochondria are essential for producing the ATP needed for various cellular processes, ensuring the plant’s overall health and vitality.
4. What happens if mitochondria are damaged in plant cells?
Damage to mitochondria can lead to reduced energy production, impaired growth, and increased susceptibility to diseases and environmental stressors.
5. How do mitochondria contribute to plant defense mechanisms?
Mitochondria play a role in signaling pathways that activate defense mechanisms against stress, such as drought or temperature extremes, helping the plant to adapt and survive.
```
0 Response to " Discover Plant Cells Mitochondria Functions"
Post a Comment