Discover How Plants Create Food | Master Photosynthesis
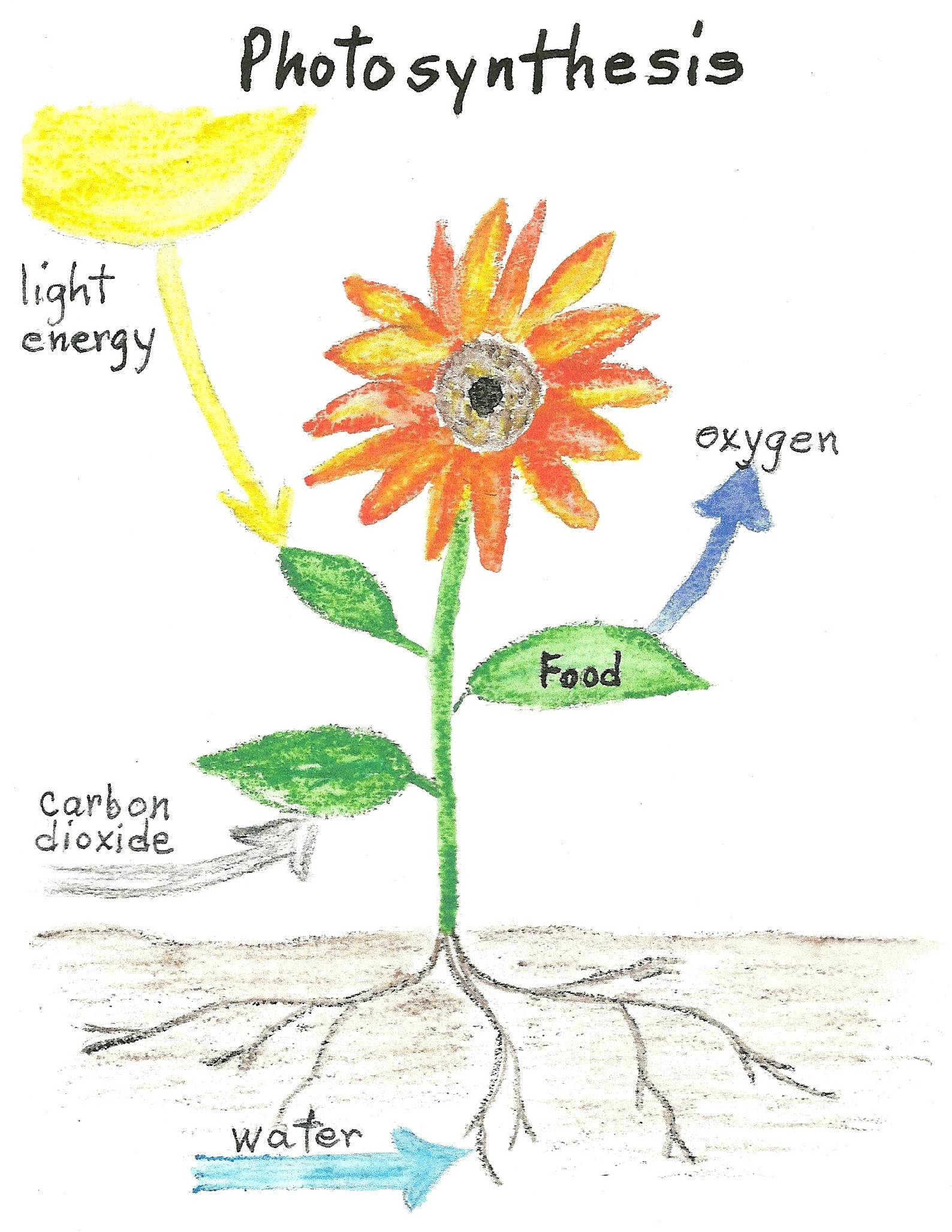
Imagine the sun, a radiant ball of fire in the sky, providing the essential energy for all life on Earth. But have you ever wondered how plants harness this sun energy to create their own food? The process is called photosynthesis, a sophisticated mechanism that converting light energy into chemical energy. Understanding how plants make food through photosynthesis is not just fascinating but also crucial for anyone interested in gardening photosynthesis or sustainable living. Let's dive in!
The Magic of Chlorophyll Photosynthesis
Chlorophyll, the green pigment in plants, is the star of the photosynthesis show. It absorbs light energy from the sun, setting the stage for the conversion of carbon dioxide plants and water into glucose. This magical pigment acts like a tiny solar panel, capturing just the right wavelengths of light to fuel the photosynthesis stages. Without chlorophyll, photosynthesis importance would dwindle, leaving plants without the means to produce plant food production. But how exactly does this remarkable process unfold?
The Photolysis: Splitting Water
The first act of photosynthesis involves the splitting of water molecules. This step is also known as photolysis, where the energy absorbed by chlorophyll breaks down water into oxygen and hydrogen. The hydrogen is used later in the process, while the oxygen is released into the atmosphere, making it available for all living organisms, including you and me. Think of it like a photosynthesis importance vs biology reciprocal exchange. Plants give us oxygen, and we provide them with carbon dioxide.
The Calvin Cycle: Fixing Carbon Dioxide
Next up is the Calvin Cycle, where carbon dioxide plants from the air is combined with hydrogen to form glucose. This stage is more like a complex factory assembly line, occurring in the chloroplasts of plant cells. The glucose, or sugar, thus produced is the primary source of energy for the plant. It's the plant's fuel, driving growth, reproduction, and all other vital functions. Envision it as a biological kitchen where raw materials like carbon dioxide and water are cooked up into a nutrient-rich meal!
The Sun Energy Plants Harvest: Light-Driven Actions
Light energy is the spark that ignites the entire process. Without it, photosynthesis would grind to a halt. The sun energy plants receive dictates the rate and efficiency of photosynthesis. This is why plants in sunny locations tend to grow faster and healthier than those in shaded areas. So, if you're into gardening photosynthesis, make sure your plants get plenty of sunlight!
The amount of light energy a plant receives determines how much food it can produce. This is crucial for understanding how plants make food and ensures that you, as a gardener, provide the optimal conditions for growth. After all, a well-fed plant is a happy plant!
The Photosynthesis Stages Unveiled
To truly master how plants make food, let's break down the photosynthesis stages more clearly:
Stage 1: Light-Dependent Reactions
In this initial stage, light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll and used to split water molecules. The light-dependent reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts. This stage produces ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate), which are essential energy carriers for the next stage.
Stage 2: Light-Independent Reactions (The Calvin Cycle)
In the second stage, the ATP and NADPH produced in the light-dependent reactions are used to fix carbon dioxide and produce glucose. This stage occurs in the stroma of the chloroplasts. The glucose is then used by the plant for growth and energy, or stored for later use. This is where the raw materials are transformed into the food that sustains the plant's life.
Why Does Photosynthesis Matter?
Photosynthesis importance cannot be overstated. It's the foundation of the food chain, providing the primary source of food for all herbivores, which in turn feed carnivores. Without photosynthesis, there would be no food for animals or humans. It's the cornerstone of life on Earth and is this remarkable process that sustains ecosystems and supports biodiversity. So, next time you see a plant basking in the sun, remember that it's not just soaking up light; it's creating the very food that keeps our world alive! Through photosynthesis stages humans take the sunlight and turn it into chemical energy.
For those who love gardening photosynthesis, understanding these stages helps in cultivating healthier plants. By providing the right conditions—adequate light, water, and nutrients—you can optimize how plants make food and watch your garden flourish!
Your Action Plan
Now that you understand how plants make food, it's time to put this knowledge into action. Pay attention to your plants' light exposure, ensure they have access to ample carbon dioxide, and keep them watered. Experiment with different lighting conditions and observe how your plants respond. Share your findings with fellow gardening enthusiasts. By mastering photosynthesis, you'll not only have a thriving garden but also a deeper appreciation for the natural world around you.
Click to Learn more about advanced gardening techniques and delve deeper into the science behind plant food production!
FAQs
1. What is the role of carbon dioxide in photosynthesis?
Carbon dioxide is a vital raw material in the photosynthesis process. Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through their leaves and use it to produce glucose, which serves as their food. Without adequate carbon dioxide, plants cannot produce the energy needed for growth and survival.
2. How does light energy influence photosynthesis?
Light energy is the driving force behind photosynthesis. It is absorbed by chlorophyll and used to split water molecules and produce ATP and NADPH, which are essential for the Calvin Cycle. The more light a plant receives, the more efficiently it can produce glucose and grow.
3. What are the stages of photosynthesis?
The photosynthesis stages consist of two main phases: the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin Cycle. The light-dependent reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes and produce ATP and NADPH. The Calvin Cycle, occurring in the stroma, uses these energy carriers to fix carbon dioxide and produce glucose.
4. Why is photosynthesis important?
Photosynthesis importance lies in its role as the primary source of food for all organisms. It produces glucose, which is the energy source for plants and the foundation of the food chain. Additionally, photosynthesis releases oxygen into the atmosphere, supporting the respiration of all aerobic organisms.
5. How can I improve photosynthesis in my garden?
To improve photosynthesis in your garden, ensure your plants receive adequate sunlight, have access to sufficient carbon dioxide, and are well-watered. Regularly monitor and optimise these conditions to support vigorous plant growth and health.
```
0 Response to " Discover How Plants Create Food | Master Photosynthesis"
Post a Comment