Practical Carbon Farming Techniques
Imagine transforming your farm into a thriving ecosystem that not only produces abundant, healthy crops but also helps combat climate change. Sounds like a win-win, right? This is the promise of carbon farming methods, a revolutionary approach to agriculture that focuses on sequestering carbon in soils and vegetation. Join us as we dive into the world of organic carbon farming and explore how these techniques can enhance soil sustainability while mitigating climate change.
What is Carbon Farming?
Carbon farming is more than just a trend; it’s a holistic approach to agriculture that prioritizes ecosystem restoration and carbon farming benefits by locking carbon in the soil. This practice not only improves soil health and fertility but also reduces the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere—making it a critical tool for climate change mitigation.
The Science Behind Carbon Farming
Understanding Soil Carbon
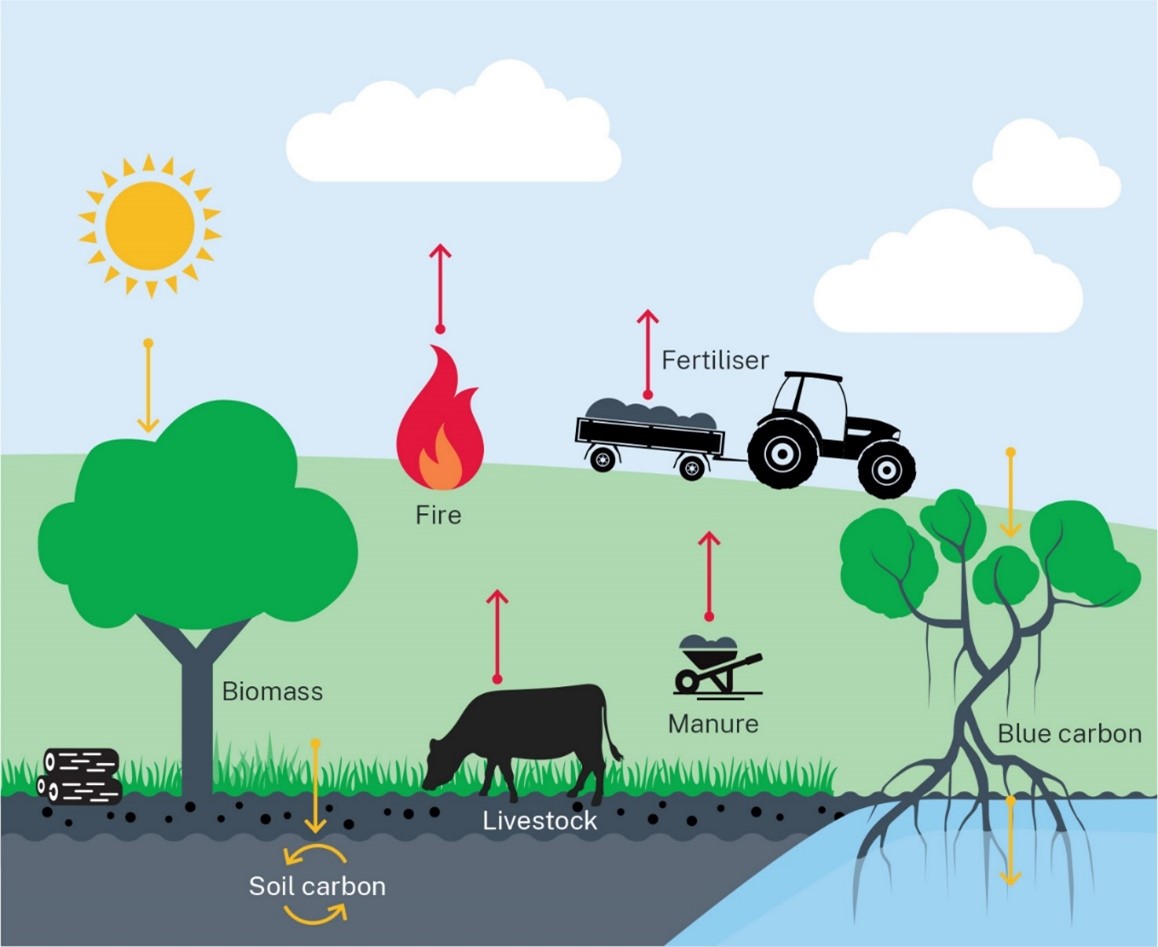
Soil is a complex ecosystem teeming with microbial life that plays a crucial role in carbon sequestration. When plants photosynthesize, they convert atmospheric carbon into organic matter, which is then transferred to the soil through roots and litter. This organic matter builds soil structure, improves nutrient availability, and supports a diverse range of microorganisms. Carbon farming leverages this natural process to increase soil organic carbon, thereby enhancing soil sustainability.
But how does carbon farming work in practice? Let's delve into some practical carbon farming methods that farmers and gardeners can implement right away.
Practical Carbon Farming Methods
Cover Cropping: A Shield for Your Soil
Why let your soil lie bare when you can give it a protective blanket? Cover cropping is one of the most effective carbon farming methods. By planting cover crops like clover, vetch, or rye, you can prevent soil erosion, suppress weeds, and add organic matter to the soil. These plants grow during fallow periods, capturing carbon and releasing it into the soil when they decompose. Think of it like a natural mulch that feeds and protects your soil.
No-Till Farming: Leave the Soil Alone
Traditional farming practices often involve tilling the soil, which disrupts soil structure and releases stored carbon into the atmosphere. No-till farming, on the other hand, leaves the soil undisturbed, preserving microbial communities and maintaining soil carbon. This method involves planting seeds directly into the residues of the previous crop, reducing soil disruption and enhancing carbon sequestration. It’s like leaving your garden untouched so that it can flourish on its own.
Composting: Nature’s Recycling
Composting is the ultimate recycling technique for organic materials. By transforming kitchen scraps, manure, and plant residues into nutrient-rich compost, you provide your soil with a steady supply of organic carbon. This improves soil structure, water retention, and fertility, making it easier for plants to grow. It’s akin to feeding your soil a rich, nutritious meal that it can easily digest.
Rotational Grazing: Moving Livestock for Healthy Pastures
Rotational grazing is a method where livestock are moved between different pastures, allowing forested areas to regenerate. This practice promotes the growth of diverse plant species, which in turn increases soil organic carbon. It’s like giving your pastures a vacation, allowing them to recover and become even more productive. By using proper grazing techniques, farmers can enhance soil health and carbon sequestration while maintaining productive livestock operations.
Agroforestry: Trees and Crops in Harmony
Agroforestry integrates trees with crops or livestock, creating a diverse and resilient ecosystem. Trees sequester carbon from the atmosphere, and their roots improve soil structure and water retention. Additionally, trees provide shade and shelter for crops and livestock, enhancing overall productivity. It’s like creating a harmonious community where each member benefits the others, resulting in a healthier, more productive landscape.
These carbon farming methods are just the beginning. With innovative techniques and technologies, farmers can further accelerate carbon sequestration and soil sustainability.
The Carbon Farming Benefits
Besides combating climate change, carbon farming methods offer a plethora of benefits. These include increased crop yields, improved soil resilience, and reduced reliance on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. But perhaps the most compelling reason to adopt carbon farming is the opportunity to contribute to global climate change mitigation efforts. By sequestering carbon in soils, farmers can help lower atmospheric carbon dioxide levels, making a tangible difference in the fight against climate change.
Overcoming Challenges in Carbon Farming Adoption
While the benefits of carbon farming are clear, adoption can face challenges. Financial constraints, lack of knowledge, and resistance to change are common barriers. However, with support from government programs, educational resources, and community initiatives, more farmers can embrace carbon farming methods. Organizations like the NRCS (Natural Resources Conservation Service) offer valuable resources and assistance for farmers looking to implement carbon farming techniques. Check out their guide on carbon sequestration for more information.
The Future of Carbon Farming
As awareness of climate change grows, so does the demand for sustainable agricultural practices. Carbon farming methods are at the forefront of this movement, offering a practical and effective way to enhance soil sustainability and mitigate climate change. By adopting these techniques, farmers can not only improve their yields and soil health but also contribute to a greener, more sustainable future.
So, why wait? Embrace carbon farming methods today and watch your farm thrive. Let’s create a world where agriculture and environmental stewardship go hand in hand. Click here to learn more about carbon farming and start your journey towards sustainable farming practices.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between traditional farming and carbon farming?
Traditional farming often focuses on maximizing immediate yields through chemical inputs and tillage, which can degrade soil health and release stored carbon. Carbon farming, on the other hand, prioritizes building soil organic matter and sequestering carbon, leading to long-term soil sustainability and climate change mitigation.
2. Can small-scale farmers benefit from carbon farming methods?
Absolutely! Carbon farming methods like cover cropping, composting, and rotational grazing can be easily adapted to small-scale and backyard farming practices. In fact, smaller operations often have more flexibility to implement these techniques.
3. Are there any government programs supporting carbon farming?
Yes, several government programs offer financial and technical assistance for farmers adopting carbon farming methods. The NRCS, for example, provides resources and support for soil health practices and carbon sequestration. You can visit their website to learn more about available programs and resources.
4. How does carbon farming impact water retention in the soil?
Carbon farming methods improve soil structure and organic matter content, which enhances water retention. Healthy soils with high organic carbon can hold more water, reducing runoff and erosion, and making them more resistant to droughts.
5. What role does biodiversity play in carbon farming?
Biodiversity is crucial in carbon farming as it promotes a healthy ecosystem. A diverse range of plants, animals, and microorganisms contributes to soil health, nutrient cycling, and carbon sequestration. Practices like agroforestry and rotational grazing increase biodiversity, making the ecosystem more resilient.
```
0 Response to " Practical Carbon Farming Techniques"
Post a Comment