How to Save Seeds from Your Garden Plants: A Step-by-Step Guide

Gardening is more than just a hobby; it's a journey of nurturing life from the ground up. Imagine the satisfaction of not only growing your own produce but also saving seeds to continue the cycle year after year. It's like creating your own little ecosystem, a legacy of sorts. So, are you ready to become a seed saver? Let's dive into the world of seed collection and plant reproduction with this comprehensive guide on how to save seeds from your garden plants.
Why Save Garden Seeds?
Saving seeds is a rewarding practice that offers numerous benefits. It's economical, as you won't need to purchase new seeds every year. It's also a great way to preserve heirloom varieties and adapt plants to your specific climate. Plus, it's an engaging and educational experience that connects you deeply with the natural world.
Understanding Plant Reproduction
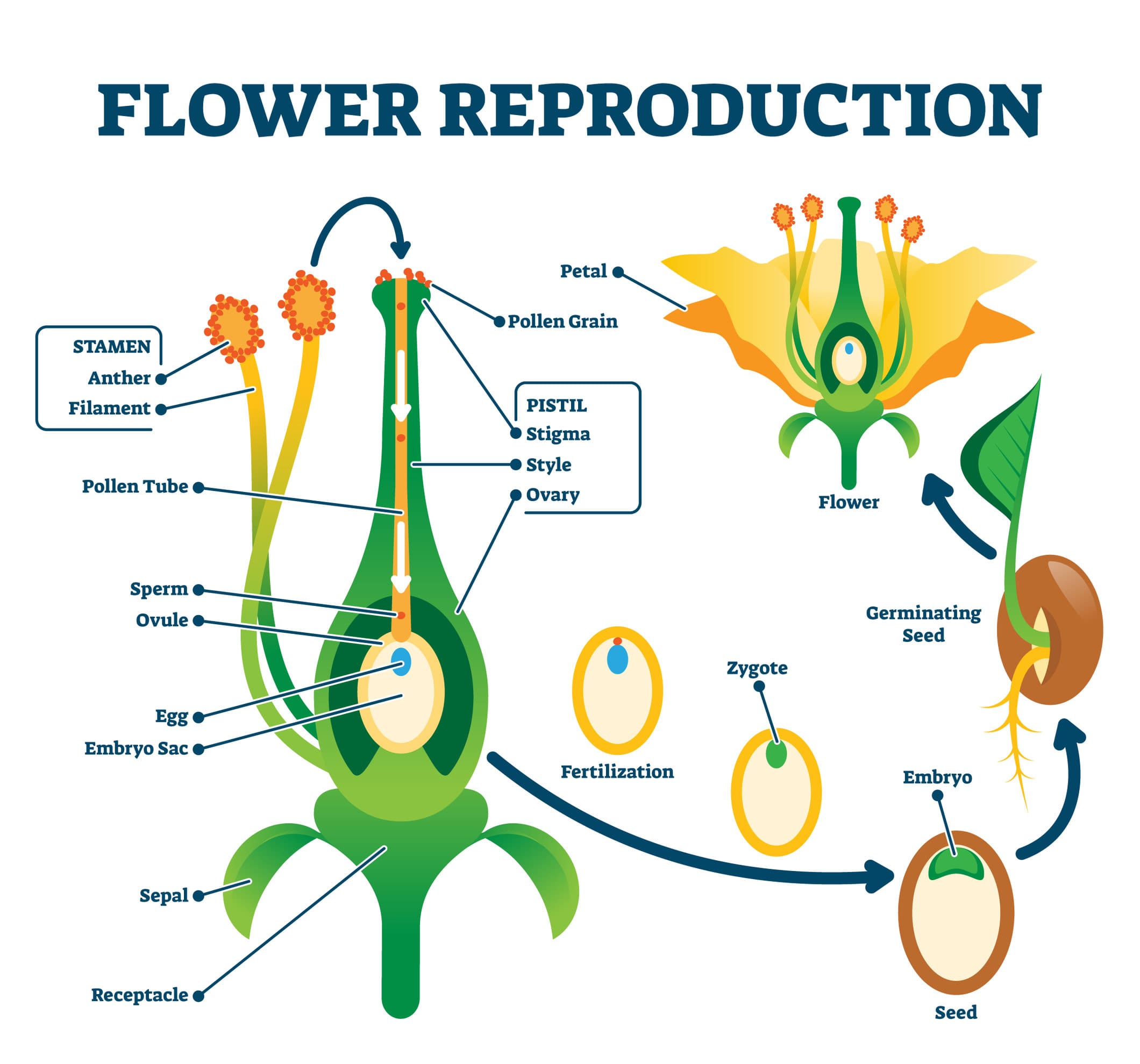
Before we delve into the process, it's crucial to understand plant reproduction. Plants can reproduce sexually through seeds or asexually through methods like cuttings or division. For seed saving, we focus on sexual reproduction, where pollination leads to the formation of seeds.
Step-by-Step Guide to Saving Garden Seeds
1. Choose the Right Plants
Not all plants are suitable for seed saving. Hybrid plants, for instance, won't produce seeds that resemble the parent plant. Instead, opt for open-pollinated or heirloom varieties, which breed true to type.
2. Timing is Key
Knowing when to collect seeds is vital. Generally, you should wait until the plant has fully matured and the seeds are ripe. This is usually after the plant has flowered and the fruit or seed pod has dried out.
3. Seed Collection Techniques
Different plants require different seed collection methods. Here are a few common techniques:
Dry Method
For plants like beans, peas, and lettuce, allow the seed pods to dry on the plant. Once dry, you can easily collect the seeds by shaking the pods into a container.
Wet Method
For fleshy fruits like tomatoes and cucumbers, the wet method is more suitable. Scoop out the seeds along with the pulp and place them in a jar with water. Let this mixture ferment for a few days, then rinse the seeds clean and dry them.
4. Cleaning and Drying Seeds
After collection, seeds need to be cleaned and dried. Remove any chaff or debris, then spread the seeds out on a flat surface to dry. Proper drying is crucial to prevent mold and ensure good germination rates.
5. Seed Storage
Proper storage is essential for maintaining seed viability. Store your seeds in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight. Airtight containers or glass jars are ideal for this purpose.

Tips for Successful Seed Germination
Once you've saved your seeds, the next step is germination. Here are some tips to ensure successful seed germination:
- Soil Preparation: Use well-draining, nutrient-rich soil.
- Watering: Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged.
- Light: Some seeds need light to germinate, while others prefer darkness. Research the specific needs of your seeds.
- Temperature: Maintain the optimal temperature for germination, which varies by plant species.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Seed saving isn't without its challenges. Common issues include low germination rates, mold, and pest damage. To mitigate these problems, ensure proper drying and storage, and consider using natural pest repellents.
The Joy of Garden Harvest
Saving seeds is just the beginning. The real joy comes from the garden harvest, where you reap the fruits of your labor. There's nothing quite like biting into a tomato you grew from seeds you saved yourself. It's a full-circle experience that's deeply satisfying.
Conclusion
Saving seeds from your garden plants is a rewarding endeavor that connects you with the natural world in a profound way. By understanding plant reproduction, timing your seed collection right, and storing your seeds properly, you can create a sustainable garden that thrives year after year. So, why not give it a try? Your garden will thank you, and so will your wallet. Happy seed saving!
FAQs
Can I save seeds from hybrid plants?
- While you can save seeds from hybrid plants, they won't produce plants identical to the parent. Hybrid seeds are a result of controlled pollination, and their offspring can vary widely.
How long can I store seeds?
- The lifespan of seeds varies by species. Generally, seeds can be stored for 1-5 years, but some can last much longer with proper storage conditions.
What is the best temperature for seed storage?
- Seeds should be stored in a cool place, ideally between 32-41°F (0-5°C). A refrigerator can be a good option, but avoid freezing temperatures.
How do I know if my seeds are viable?
- A simple germination test can help determine seed viability. Place a few seeds in a moist paper towel, seal them in a plastic bag, and wait for them to sprout.
Can I save seeds from diseased plants?
- It's generally not recommended to save seeds from diseased plants, as some diseases can be seed-borne and may affect future plants.
For more detailed information, you can visit resources like the Seed Savers Exchange and the International Seed Saving Institute. These organizations provide extensive guides and support for seed savers of all levels.
0 Response to "How to Save Seeds from Your Garden Plants: A Step-by-Step Guide"
Post a Comment