Discover Why Plants Are Beautifully Green
The world around us is a symphony of colors, but none are as ubiquitous or as vital to our existence as that brilliant, verdant hue: green. Have you ever paused to wonder why plants are green? What's underneath this universal color that meters life on Earth? Dive into the intricate world of plant photosynthesis and pigments to uncover the answers to these questions!
Unraveling the Plant Chlorophyll Mechanism
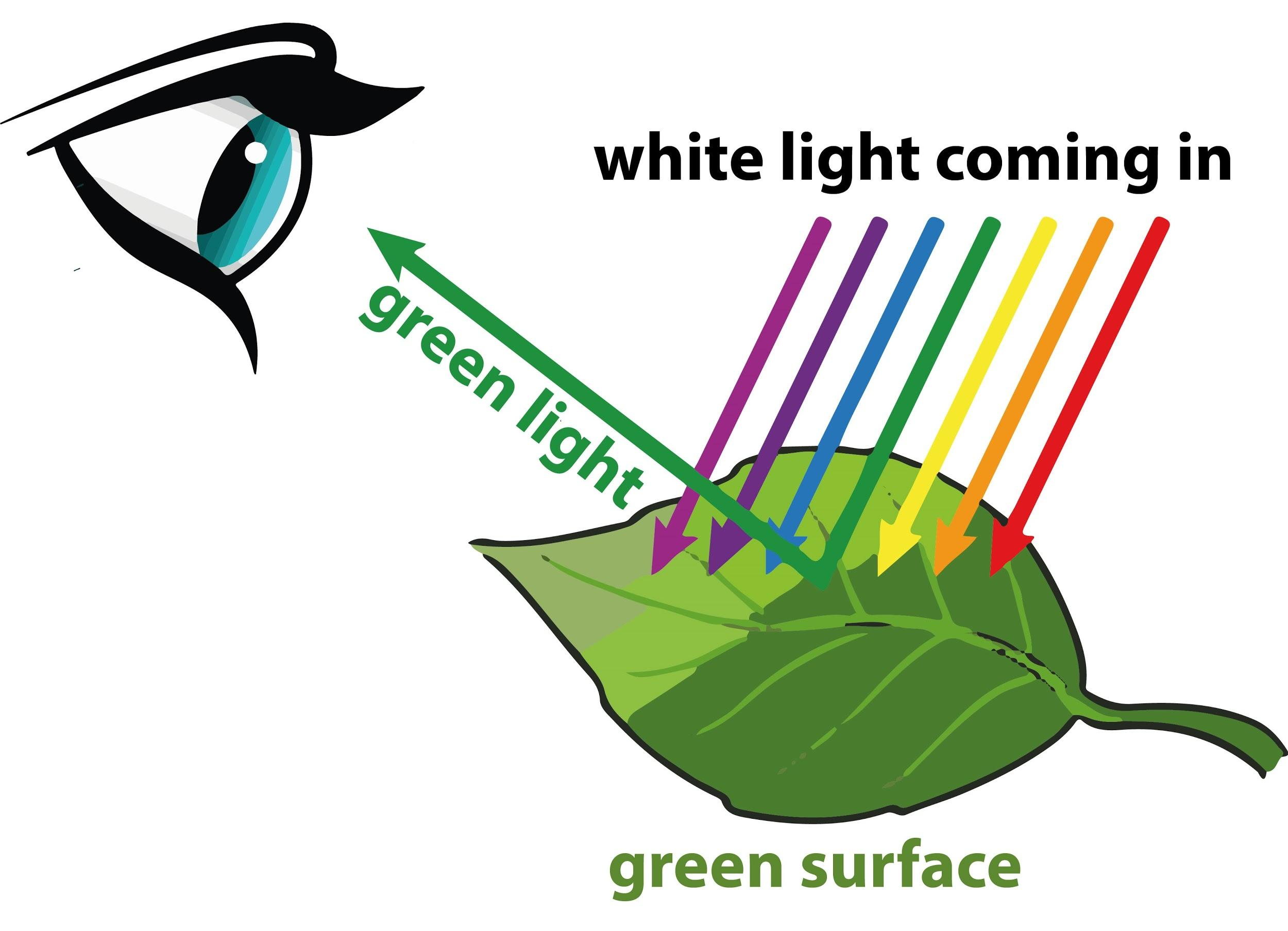
At the heart of why plants are green lies the Plant Chlorophyll Mechanism. Chlorophyll, the primary pigment in plants, plays a crucial role in the Photosynthesis Process. It absorbs light, particularly blue and red wavelengths, and reflects green light, which is why we perceive leaves as green.
Think of chlorophyll as the plant's engine. Just as a car engine converts fuel into motion, chlorophyll converts sunlight into chemical energy. This Sunlight Convertion is the backbone of Photosynthesis, enabling plants to produce oxygen and glucose, vital for their Energy Production.
The Magic of Photosynthesis
Let’s break down the Photosynthesis Process. When a plant absorbs sunlight, it triggers a series of reactions within the chlorophyll. These reactions split water molecules, releasing oxygen and producing hydrogen ions that combine with carbon dioxide to form glucose. It’s a fascinating natural mechanism that fuels the entire ecosystem.
Imagine if plants couldn’t perform this magic trick of converting sunlight into energy. Our world would be a dramatically different place. The air we breathe, the food we eat, and the vast biodiversity we enjoy all owe their existence to this incredible process.
Plant Pigments: Nature’s Palette
While chlorophyll is the star player in the Photosynthesis Process, it’s not alone. Plant pigments are the artists painting nature's canvas. There are several types, including carotenoids, anthocyanins, and xanthophylls, each contributing to the colors we see in leaves, flowers, and fruits.
Carotenoids, for instance, absorb blue and green light, reflecting orange and yellow hues. You're familiar with carrots, right? They get their vibrant orange color from carotenoids. But why aren't plants orange and yellow primarily when they possess these pigments?
Because chlorophyll is dominant and masks these colors. When chlorophyll starts to break down, as in the fall, the underlying carotenoids become visible. It's like peeling an onion to reveal the layers beneath. This dynamic interplay of pigments adds depth and beauty to the natural world, making it ever-changing and ever-captivating.
The Role of Sunlight
Sunlight is the lifeblood of plants. Through the Sunlight Convertion process, plants transform this energy into the chemical bonds of glucose and oxygen. This Energy Production is not just about sustaining the plant; it's about sustaining the entire ecosystem.
Every time you see a green leaf, remember that it's a tiny factory converting sunlight into the energy that sustains life on Earth. It’s almost like plants are nature’s solar panels, harvesting sunlight and converting it into useable energy.
Benefits and Implications
Understanding why plants are green has broader implications. It gives us insight into the intricate balance of life and the essential role of plants in our ecosystem. Plants not only provide us with food and oxygen but also mitigate climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide.
Moreover, studying plant pigments and the Photosynthesis Process can lead to innovations in renewable energy. By mimicking these natural mechanisms, scientists are developing more efficient ways to convert sunlight into Energy Production, paving the way for a greener future.
Conclusion
So, the next time you marvel at a lush, green landscape, remember the intricate science behind it. From the Chlorophyll Mechanism to the diverse Plant Pigments, every green hue reveals a story of life, energy, and sustainability. Understanding why plants are green connects us to the profound, interconnected web of life on Earth.It's not just about aesthetics; it's about the very essence of our existence.
We invite you to delve deeper into the fascinating world of plant biology. Learn about the Plant Chlorophyll Mechanism and the Photosynthesis Process. Discover how plants convert sunlight and produce energy, sustaining life as we know it. Check out this resource provided by Britannica on chlorophyll for more detailed information and feel the utter beauty of nature.
Join us in celebrating the green wonder of the world and exploring the science behind it. Click Here to explore more about the diverse world of plant pigments!
FAQs
1. How exactly do plants convert sunlight into energy?
Plants convert sunlight into energy through the process of photosynthesis. The chlorophyll in their leaves absorbs light energy, triggering chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
2. Why do plants appear green when chlorophyll absorbs other colors?
Chlorophyll absorbs blue and red light, reflecting green light. This reflected green light is what our eyes perceive, making plants appear green.
3. Besides chlorophyll, what other pigments do plants have?
Plants have various pigments, including carotenoids (yellow and orange), anthocyanins (red and purple), and xanthophylls (yellow). These pigments become visible when chlorophyll breaks down, as seen in autumn leaves.
4. How does photosynthesis benefit the ecosystem?
Photosynthesis is crucial for the ecosystem as it produces oxygen and glucose. Oxygen is essential for respiration in most living organisms, while glucose is a primary energy source for plants and animals.
5. Can understanding photosynthesis benefit renewable energy?
Yes, studying photosynthesis can inspire innovations in renewable energy. By mimicking the natural mechanisms of photosynthesis, scientists are developing more efficient ways to convert sunlight into usable energy, such as solar cells and bio-fuels.
```
0 Response to " Discover Why Plants Are Beautifully Green"
Post a Comment