Master Regenerative Farming Principles and Methods
Imagine a world where farming not only sustains life but also enhances the environment. Where the very act of growing food rebuilds soils, enhances biodiversity, and even combats climate change. Welcome to the world of regenerative agriculture principles and methods. You might be asking, how can nature be restored while steadily increasing yields? The answer lies in embracing the synergistic dance between natural farming methods, ecological agriculture, and soil regeneration techniques. Let’s dive deep into how regenerative agriculture principles and methods can transform our food system and create a sustainable future.
Understanding Regenerative Agriculture Principles
At its core, regenerative agriculture is about working with nature, not against it. It’s akin to a finely-tuned orchestra where each instrument (crop, soil, water, and microbes) plays a critical role in creating harmony. So, what are the key principles that set regenerative agriculture apart?
Minimum Soil Disturbance: Cultivating a Living Sensor
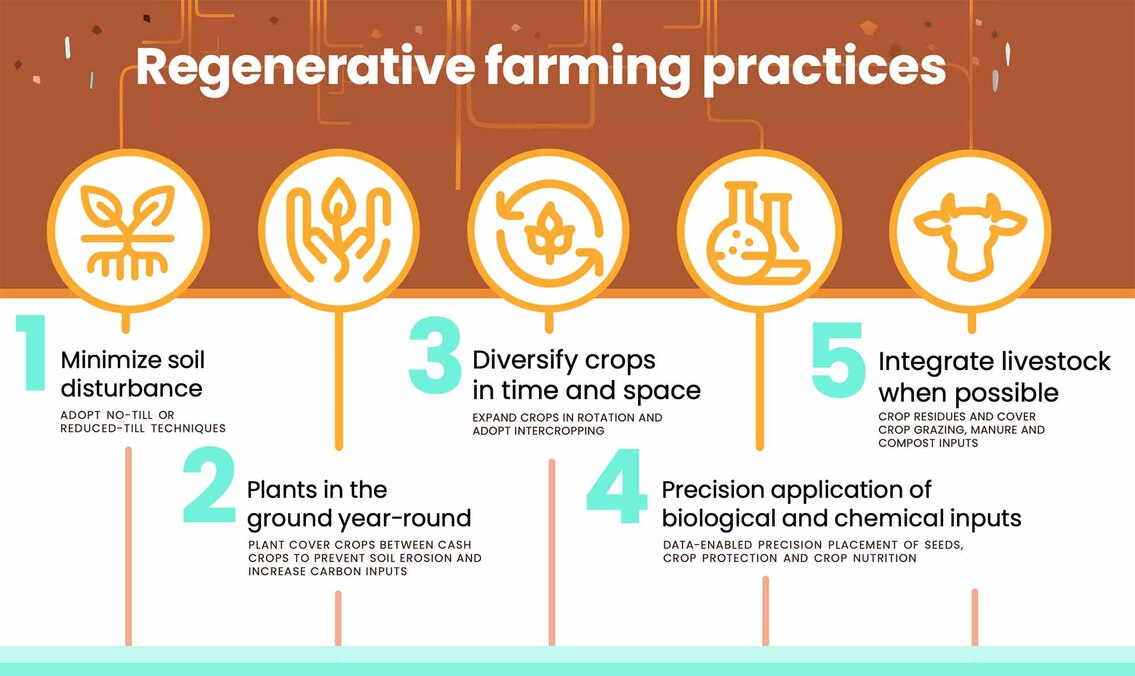
Traditional farming often involves tilling the soil, a practice that can disrupt soil structure and microbial communities. In regenerative agriculture, we aim to minimize soil disturbance. Think of soil as a living sensor that can feel and respond to changes. By reducing tillage, we allow the soil to stay healthy and robust. This in turn, promotes sustainabile crop yield and improves the soil’s ability to sequester carbon. So, why burn your field when you can nurture it?
Diverse Planting: Nature’s Biodiversity Blueprint
Monoculture farming, where a single crop is grown extensively, can lead to soil depletion and reduced biodiversity. Regenerative agriculture, on the other hand, champions crop diversity. Plant a variety of crops within the same area. This diverse planting mimics natural ecosystems and fosters a richer soil microbiome, reducing pest outbreaks and boosting the overall health of the ecosystem. The more species we cultivate, the more resilient our agriculture becomes.
Animal Integration: The Pasture’s Circle of Life
Animals are integral to regenerative agriculture. By integrating livestock into the farming cycle, we create a closed-loop system where manure enriches the soil, and crops feed the animals. Think of it as a circular dance where everything connects and supports each other. For instance, rotations of pastured poultry and ruminants can improve soil fertility and structure, leading to healthier and more nutritious food. Moreover, it contributes to the well-being of livestock, which must always be prioritized as integral parts of the farm family.
Exploring Regenerative Farming Methods
Now that we have the principles under our belts, let’s delve into the specific regenerative farming methods that bring these principles to life.
Cover Cropping: The Unsung Hero of Soil Health
Cover cropping is one of the most effective soil regeneration techniques. These crops are planted during the off-season to protect the soil from erosion, suppress weeds, and enrich the soil with organic matter. Legumes, grasses, and brassicas are common choices. They help retain moisture, promote soil biodiversity, and act as a living mulch. It’s like giving the soil a warm blanket during the winter, so it can wake up refreshed and ready to go in the spring. By enhancing soil health and biodiversity, cover cropping ensures sustainabile crop yield year after year.
Permaculture: Designing with Nature’s Wisdom
Permaculture is another key method in regenerative agriculture, emphasizing the integration of natural farming methods with sustainable systems. By observing nature’s patterns and mimicking them, we can create highly productive and resilient farms. Permaculture also focuses on the ethical use of resources and the cultivation of healthy, diverse ecosystems. Just as nature thrives on balance and resilience, so too can our farms.
Holistic Grazing: Rebuilding the Pasture
Holistic grazing involves strategically moving livestock through pastures to mimic wild herds’ natural patterns. This practice allows plants to recover fully between grazing periods, preventing overgrazing and promoting vigorous growth. It’s akin to giving your lawn a chance to breathe and regenerate after being walked on. With proper management, holistic grazing can significantly improve soil structure, nutrient cycling, and overall pasture health. Moreover, it contributes to
carbon sequestration, helping in the fight against climate change.
The Science Behind Regenerative Agriculture
While the principles and methods of regenerative agriculture are rooted deeply in ancient wisdom, they are also backed by modern science. Researchers have shown that regenerative practices can sequester carbon from the atmosphere, thus mitigating the impacts of climate change. They’ve also documented improved soil structure, enhanced water retention, and increased biodiversity. Let’s explore some of these findings in more detail.
The Role of Soil Health in Climate Mitigation
The soil is a vast carbon sink. Healthy soils can sequester significant amounts of carbon, helping to reduce atmospheric CO2 levels. According to the [[Rodale Institute]](https://rodaleinstitute.org/research/white-papers/regenerative-organic-agriculture-and-climate-change/), regenerative organic agriculture practices can help mitigate climate change. By promoting soil health, regenerative agriculture not only produces food but also acts as a solution to environmental challenges.
Enhancing Biodiversity for a Resilient Ecosystem
Regenerative agriculture fosters biodiversity by creating habitats for a wide range of plants and animals. This diversity is crucial for a resilient ecosystem. It reduces the need for pesticides and fertilizers, as natural predators and beneficial microbes thrive in diverse environments. It’s like having a well-stocked medicine cabinet where each remedy supports the overall health of the body. The more diverse our farms, the better equipped they are to withstand pests, diseases, and environmental stresses.
According to [[FAOSTAT]](http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#home), regenerative agriculture practices can significantly improve the soil and ecological balance, making regions more resilient against climate and ecological challenges.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications of Regenerative Agriculture
To see regenerative agriculture in action, let’s look at some real-world case studies. These stories showcase how farmers are implementing regenerative principles and methods and achieving remarkable results.
Polyface Farms: The Modern Homestead
Joel Salatin’s Polyface Farms in Virginia is a shining example of regenerative agriculture. By integrating poultry, cattle, and pigs into a carefully managed system, Polyface Farms has created a closed-loop operation where waste from one animal becomes nutrients for another. This holistic approach has not only improved soil health but also increased profitability and sustainability. Visit [[Polyface Farms]](https://polyfacefarms.com/) to explore their journey in regenerative agriculture.
The Savory Institute: Transforming Drylands
The Savory Institute, founded by Allan Savory, focuses on holistic management and holistic grazing. Their work in regenerating degraded landscapes, particularly drylands, has shown incredible results. By mimicking natural herd movements and resting periods, they have successfully restored grasslands, sequestered carbon, and improved water retention. Check out their [[success stories]](https://savory.global/case-studies/) to see the transformative power of regenerative agriculture.
Getting Started with Regenerative Agriculture
So, you’re convinced of the benefits of regenerative agriculture principles and methods. You want to dive in, but where do you start? Here are some steps to help you get started on your regenerative farming journey.
Assess Your Soil: The Foundation of Success
Start by getting a comprehensive soil test. Understand your soil’s health, structure, and fertility. This will guide your decisions on which regenerative practices to implement. Think of it as a health check-up for your land. The better you understand your soil, the better equipped you are to nurture it.
Choose Your Cover Crops: Starters for Soil Health
Select cover crops that align with your region and soil needs. Legumes for nitrogen, brassicas for pest control, and grasses for structure—each has a role to play. Start small, perhaps with a test patch, and observe the results before scaling up. It’s like starting a garden—you plant a few seeds, watch them grow, and learn as you go.
Integrate Livestock: Movement and Manure
If you have or can acquire livestock, integrate them into your farming system. Start with grazing plans that consider herd size, forage availability, and rest periods. It’s a balancing act, but the benefits are immense. Healthy soils, improved forage, and happy animals—all interconnected in the regenerative cycle.
Conclusion
Mastering regenerative agriculture principles and methods is not just about growing food; it’s about nurturing life. It’s about creating a symbiotic relationship with nature where the land gives back as much as it receives. From cover cropping to holistic grazing, each practice plays a critical role in building resilience and sustainability. Whether you’re a small-scale farmer or a large agricultural corporation, embracing regenerative agriculture can transform your operations and contribute to a healthier planet.
So, are you ready to embark on this regenerative journey? Start small, stay patient, and always observe and adapt. Your land, your crops, and your community will thank you. The future of agriculture is regenerative, and it’s within your reach. Click here to schedule a free consultation and learn more about how regenerative agriculture can benefit you.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary goal of regenerative agriculture principles and methods?
The primary goal of regenerative agriculture is to enhance soil health, biodiversity, and ecosystem resilience while producing sustainabile crop yields. This approach aims to create a harmonious balance between agricultural production and environmental sustainability.
How does cover cropping contribute to soil health?
Cover cropping protects the soil from erosion, suppresses weeds, and enriches the soil with organic matter. By promoting soil biodiversity and improving water retention, cover cropping ensures the soil stays healthy and robust, which is essential for sustainabile crop yield and carbon sequestration.
Can regenerative agriculture help combat climate change?
Yes, regenerative agriculture practices can significantly sequester carbon from the atmosphere, thereby mitigating the impacts of climate change. Healthy soils act as vast carbon sinks, helping to reduce atmospheric CO2 levels and contribute to ecological agriculture.
What role do animals play in regenerative farming methods?
Animals are integral to regenerative agriculture as they contribute to nutrient cycling and soil health. Through holistic grazing and manure deposition, animals enrich the soil and promote vigorous plant growth, leading to a more resilient and productive ecosystem.
How can I get started with regenerative agriculture on my farm?
To get started with regenerative agriculture, begin by assessing your soil health, choosing appropriate cover crops, and integrating livestock if possible. Start with small-scale implementations and observe the results before scaling up. This approach allows you to learn and adapt as you go, ensuring a successful transition to regenerative practices.
```
0 Response to " Master Regenerative Farming Principles and Methods"
Post a Comment